Available with Spatial Analyst license.
Summary
Divides the values of two rasters on a cell-by-cell basis.
Illustration
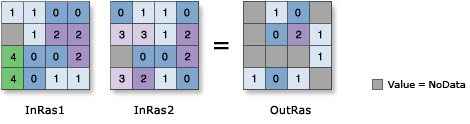
Discussion
When using an operator with a raster input the result will be a raster. However, if all inputs are numbers, then the result is a number.
When multiple operators are used in an expression, they are not necessarily executed in left-to-right order. The operator with the highest precedence value will be executed first. For more information on operator precedence, see operator precedence table. You can use parentheses to control the execution order.
The order of input is relevant for this operator.
When a number is divided by zero, the output result is NoData.
The exact division technique used by this operator depends on the application being used when performing it.
In ArcMap, the divide operator employs the integer division technique of Python 2, where only the integer quotient is retained. If both inputs are integers, the operator performs an integer division, and the output will be an integer. For example, if 3 is divided by 2, the output is 1, or if -3 is divided by 2, the output is -2. If either input is of floating-point type, the divide operator performs a floating-point division, and the output will be a floating-point value. For example, if 3 is divided by 2.0, the output is 1.5.
In ArcGIS Pro, the floating-point division of Python 3 is always used for this operator, and the output will always be a floating-point value. For example, if 3 is divided by 2, the output is 1.5.
Note:
Keep this difference in mind if you are migrating from ArcGIS Desktop to ArcGIS Pro, or you will be working in a mixed environment of both. You can use the // (Integer Division) operator if it is important to maintain the integer output.
Another way to perform the divide operation is a /= b, which is an alternative way to write a = a / b.
Syntax
in_raster_or_constant1 / in_raster_or_constant2
| Operand | Explanation | Data Type |
in_raster_or_constant1 | The input whose values will be divided by the second input. If the first input is a raster and the second is a scalar, an output raster is created with each input raster value being divided by the scalar value. | Raster Layer | Constant |
in_raster_or_constant2 | The input whose values the first input are to be divided by. If the first input is a scalar and the second is a raster, an output raster is created, with each input raster value being divided into the scalar value. | Raster Layer | Constant |
Return Value
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| out_raster | The output raster object. The cell values are the quotient of the first input raster (dividend) divided by the second input (divisor). | Raster |
Code sample
This sample divides the values of the first input raster by the second.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
outDivide = Raster("degs") / Raster("negs")
outDivide.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outdivide")This sample divides the values of the first input raster by the second.
# Name: Op_Divide_Ex_02.py
# Description: Divides the values of two rasters on a cell-by-cell basis
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inRaster01 = Raster("elevation")
inRaster02 = Raster("landuse")
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Execute Divide
outDivide = inRaster01 / inRaster02
# Save the output
outDivide.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outdivide2")